Presentation
With regards to Plastic Mold, choosing the right strategy is significant for upgrading your item’s presentation, quality, and cost-adequacy. This guide dives into the essential plastic Mold strategies, contrasting their highlights, benefits, and applications to assist you with settling on an educated choice for your item.
Die Casting Mold
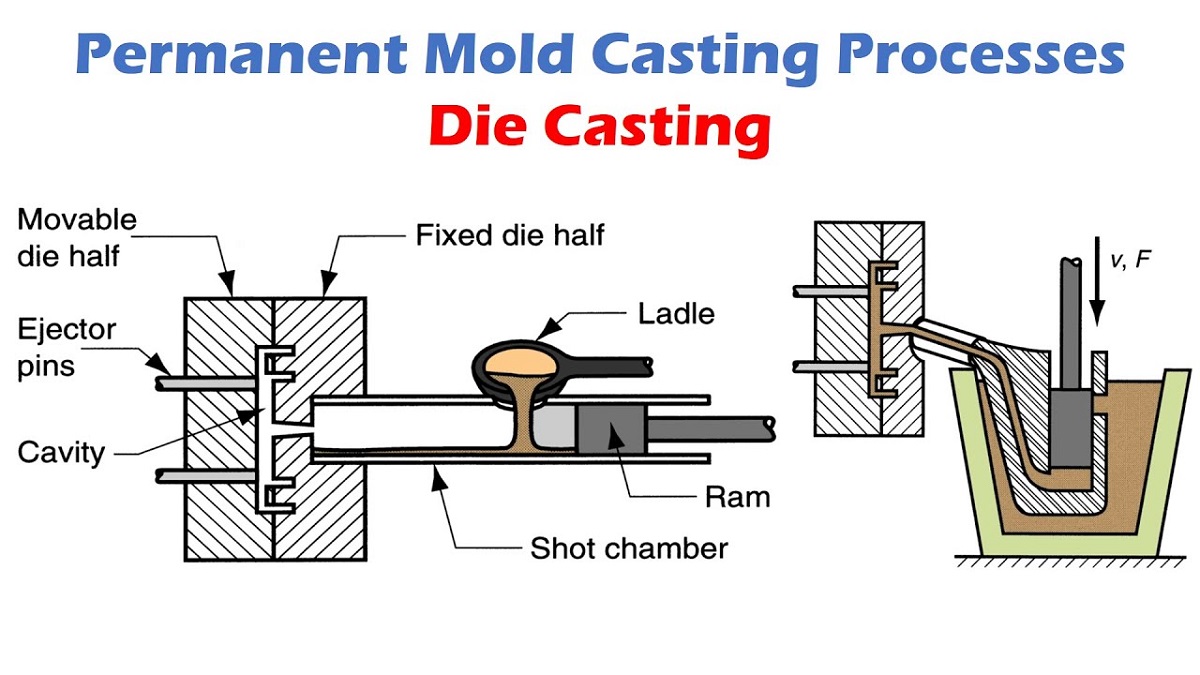
Die Casting Mold, otherwise called bites the dust, are particular apparatuses utilized in the pass on projecting cycle to shape liquid metal into exact, complex shapes. These molds are ordinarily produced using high-grade steel because of the extraordinary tension and high temperatures associated with the cycle. The Die Casting Mold cycle includes infusing liquid metal, like aluminum, zinc, or magnesium, into the shape pit under high tension. The shape comprises of two fundamental parts: the proper pass on half and the mobile bite the dust half. At the point when the liquid metal is infused, it rapidly cools and sets into the ideal shape.
The plan and development of pass on projecting molds are basic, as they straightforwardly impact the exactness, strength, and surface completion of the eventual outcome. Molds can be intended for single-pit or multi-cavity use, contingent upon the creation needs. Also, they might incorporate complex elements like ejector pins, cooling channels, and sliders to help with the creation cycle and guarantee predictable quality. Because of the significant expense and intricacy of kick the bucket projecting molds, they are normally utilized for high-volume creation runs, making them ideal for assembling parts in businesses, for example, auto, aviation, and shopper hardware.
Infusion Plastic Mold
Infusion shaping is one of the most generally utilized Plastic Mold strategies, known for its proficiency and adaptability. In this cycle, plastic pellets are warmed until they soften and are then infused into a form cavity under high tension. When cooled, the shape is eliminated, uncovering the completed part.
Benefits of Plastic Mold:
- High Accuracy and Consistency: Infusion shaping offers uncommon exactness and consistency, making it ideal for delivering multifaceted plans and high-volume creation runs.
- Financially savvy for Huge Runs: Albeit the underlying arrangement cost is high, the per-unit cost diminishes altogether with expanded creation volumes.
- Extensive variety of Materials: This strategy obliges various thermoplastics and thermosetting plastics, giving adaptability in material decision.
Burdens of Infusion Trim:
- High Starting Expenses: The making of molds can be costly, which probably won’t be appropriate for little creation runs.
- Longer Lead Times: The shape plan and assembling cycle can be tedious, possibly postponing item dispatches.
Blow Trim
Blow shaping is an interaction used to make empty plastic parts, like jugs and compartments. It includes softening plastic and framing it into a parison (a cylinder like piece of plastic). The parison is then expanded inside a form depression to shape it into the ideal structure.
Benefits of Blow Embellishment:
- Financially savvy for Enormous Volumes: Blow shaping is great for delivering high volumes of empty parts with predictable quality.
- Flexibility in Plan: It considers the making of perplexing shapes and sizes, including multifaceted designs.
Weaknesses of Blow Embellishment:
- Restricted to Empty Parts: This procedure is fundamentally appropriate for making empty things and can’t be utilized for strong aspects.
- Size Imperatives: The size of the shape depression can restrict the components of the end result.
Rotational Embellishment
Rotational embellishment, or rotomolding, includes warming a plastic material in a form while turning the shape around two opposite tomahawks. The plastic melts and covers the inside of the form, making an empty, uniform part once cooled.
Benefits of Rotational Embellishment:
- Indeed, even Wall Thickness: Rotomolding produces leaves behind reliable wall thickness, which improves strength.
- Plan Adaptability: This procedure is appropriate for huge, complex shapes that would be challenging to accomplish with other embellishment strategies.
- Drawbacks of Rotational Trim:
- Lower Creation Speed: The interaction is moderately sluggish, making it less great for high-volume creation.
- High Arrangement Expenses: The expense of molds and hardware can be huge, especially for enormous molds.
Thermoforming
Thermoforming includes warming a plastic sheet until it becomes flexible and afterward hanging it over a form. The plastic is vacuumed or pressure-framed against the form to make the last shape.
Benefits of Thermoforming:
Savvy for Low to Medium Volumes: Thermoforming is more affordable than infusion shaping for more modest creation runs.
Fast Circle back: The interaction takes into consideration quick prototyping and short lead times.
Drawbacks of Thermoforming:
Restricted to Thin-Walled Parts: This strategy is by and large appropriate for dainty walled parts and may not be great for thicker or more intricate plans.
Lower Accuracy: Thermoforming may not accomplish a similar degree of accuracy as infusion forming.
Pressure Plastic Mold
Pressure forming includes putting a pre-estimated measure of plastic material into an open shape cavity. The form is then shut, and intensity and tension are applied to fix the plastic. The outcome is a section with phenomenal layered strength and surface completion.
Benefits of Plastic Mold:
Ideal for Thermosetting Plastics: This method functions admirably with materials that go through a compound change when warmed, like thermosetting plastics.
Really great for Huge Parts: Pressure shaping is viable for creating enormous parts with complex shapes.
Drawbacks of Plastic Mold:
Longer Process durations: The interaction can be more slow contrasted with other embellishment methods, influencing creation speed.
High Tooling Expenses: The underlying expense of molds can be high, especially for complex plans.
Picking the Right Strategy for Your Item
Choosing the suitable Plastic Mold procedure relies upon different variables, including:
Material Prerequisites: Various strategies work better with explicit materials, so consider the properties of the plastic you really want.
Creation Volume: High-volume creation might legitimize the underlying expense of infusion shaping, while lower volumes could profit from thermoforming.
Part Intricacy: Perplexing or enormous parts may be more qualified to rotational trim or pressure shaping.
Cost Imperatives: Equilibrium the expense of embellishment with your financial plan and creation needs to pick the most savvy arrangement.
End
Picking the right Plastic Mold shape strategy is fundamental for streamlining item quality, execution, and cost-viability. Infusion shaping is prestigious for its accuracy and productivity, making it ideal for high-volume creation of many-sided plans yet includes high starting expenses. Blow shaping is appropriate for making empty parts like containers, offering cost-adequacy and adaptability in plan for enormous volumes. Rotational trim produces leaves behind uniform wall thickness and complex shapes however is increasingly slow high arrangement costs. Thermoforming takes into account fast prototyping and is practical for little to medium creation runs, however it is restricted to thin-walled parts. Pressure shaping succeeds with thermosetting plastics and enormous parts, furnishing magnificent layered security however accompanies longer process durations and high tooling costs. Choosing the right strategy relies upon factors like material prerequisites, creation volume, part intricacy, and financial plan, guaranteeing ideal quality and proficiency for the item.